Pre-treatment of High Salt Wastewater Zero Discharge
The key technology of zero discharge of high salt wastewater can be divided into three stages:
Pretreatment stage
Membrane treatment stage
Evaporation stage
Pretreatment stage
Hardness is divided into Total hardness, temporary hardness, and permanent hardness.
- Total hardness refers to the total amount of Ca2+and Mg2+in water.
- Temporary hardness, also known as carbonate hardness, mainly consists of Ca (HCO3) 2 and Mg (HCO3) 2. Due to the decomposition of this salt into precipitates from water after heating, it is called temporary hardness.
- Permanent hardness, also known as non carbonate hardness, mainly refers to salts such as CaSO4, MgSO4, CaCl2, MgCl2, Ca (NO3) 2, Mg (NO3) 2 in water. This type of hardness cannot be removed by heating, hence it is called permanent hardness. Hardness is an important indicator of water quality, and removing hardness from water is called water softening.
At present, water softening mainly includes Precipitation softening method, Enhanced crystallization technology, Ion exchange method, etc
Precipitation softening method
This mainly includes traditional medicament softening method and biodegradable urea carbonate precipitation method.
- Traditional pharmaceutical softening methods can be further divided into lime softening method, lime gypsum softening method, and lime soda (soda) softening method.
- The disadvantage of this type of method is that it may cause secondary pollution and the cost of reagents is high, which will increase the cost.
- The biological degradation of urea to produce carbonate precipitation method mainly utilizes a series of biochemical reactions such as enzymatic decomposition of urea to generate carbonate precipitation, which is then removed through filtration.
- The disadvantage of this method is that the concentration of ammonium ions generated during the reaction process is high, and the subsequent processing cost also increases accordingly
Enhanced crystallization technology
The basic principle of using a fluidized bed to remove hardness from water is to use gas or liquid to keep solid particles in a suspended state. The main addition of solid particles such as granular calcite (CaCO3) and quartz sand in the fluidized bed reactor not only effectively removes calcium and magnesium ions, but also recycles the precipitates containing calcium and magnesium.
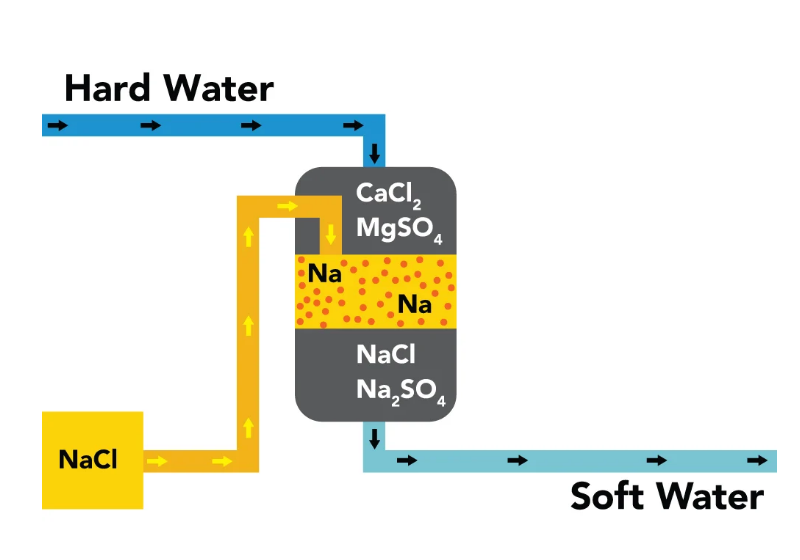
Ion exchange method
The ion exchange hardening method is mainly used to remove all or part of Mg2+and Ca2+in water before membrane treatment.
Ion exchange resin is another type of material besides hard, which is a polymer with corresponding functional groups. Feed the raw water into the ion exchange resin adsorption column, and the Mg2+and Ca2+in the water will exchange with the cations on the resin to achieve the purpose of removing hardness from the water.
Visit www.evuchina.com for more informations!