Oily Wastewater Treatment
Oily wastewater mainly comes from oil extraction and processing, petrochemical, metallurgical and mechanical industries, and maritime transportation industries. Its main components include: light hydrocarbons, heavy hydrocarbons, fuel, tar, lubricating oil, fatty oil, wax grease, soap, etc.
According to the source of oily wastewater and the different forms of oil in water, it can be divided into:Floating Oil, Dispersed Oil, Emulsified Oil, and Dissolved Oil:
- Floating Oil: A continuous oil film floats on the water surface, forming an oil film or oil layer. The oil droplet particles are relatively large, generally greater than 100 μ m。
- Dispersed Oil: Suspended and dispersed in the water phase with small oil droplets, unstable, and can aggregate into larger oil droplets to convert into floating oil. The particle size of the oil droplets is generally 10-100 μ m。
- Emulsion Oil: Due to the presence of surfactants, oil appears as an emulsion in water and the system is relatively stable. The particle size of oil droplets is extremely small, usually less than 10 μ m. Most of them are between 0.1 and 2 μ m。
- Dissolved Oil: Dispersed in a molecular state in water to form an oil-water homogeneous system, which is very stable and generally below 5-15mg/L. The particle size of oil droplets is very small, sometimes as small as a few nanometers.
Removal of Floating Oil
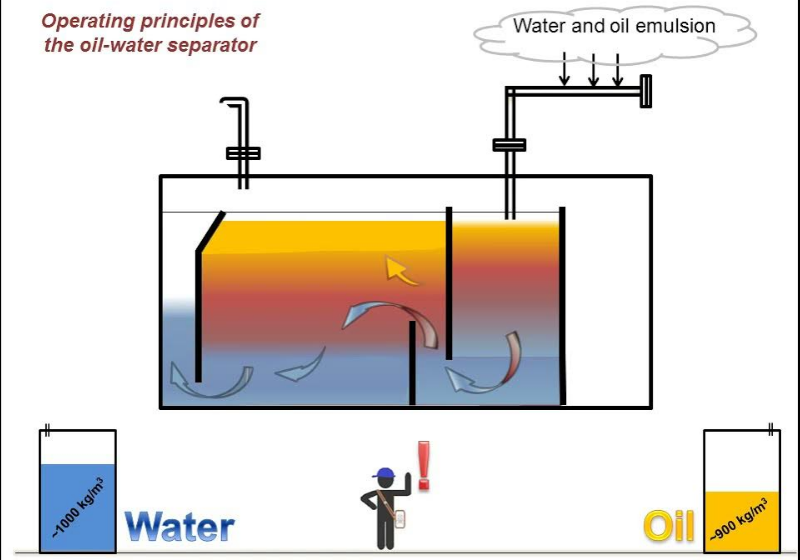
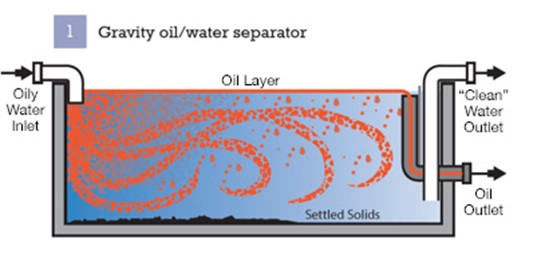
The most commonly used method for floating oil is gravity separation, which utilizes the density difference between oil and water for separation and can be used to remove particles larger than 60 μ The larger oil droplets of m and the majority of solid particles in wastewater.
The most commonly used equipment using gravity separation method is an Oil Separator, which utilizes the lighter nature of oil than water to separate oil from the water surface and skim it off. There are many forms of oil separators, mainly including horizontal flow oil separators (API), parallel plate oil separators (PP), corrugated inclined plate oil separators (CPI), and pressure difference automatic skimming devices.
Removal of dissolved oil
The content of dissolved oil in wastewater is generally low, and adsorption or biochemical methods can be used for deep treatment of dissolved oil.
Biochemical Method
There are two types of biochemical treatment for oily wastewater: Activated Sludge Method and Biofiltration Method.
- Activated Sludge Method utilizes flowing flocs and activated sludge as carriers for purifying microorganisms in an aeration tank, and decomposes organic matter by adsorbing and concentrating microorganisms on the surface of the flocs.
- Biofiltration is a process in which microorganisms attach to a fixed carrier (filter material) in a biofilter, and wastewater is dispersed from top to bottom. During the process of flowing through the surface of the filter material, organic substances in the wastewater are adsorbed and decomposed by microorganisms.
The biochemical process for treating oily wastewater is mature and has low operating costs, but it has high requirements for influent water quality and is mainly used as a deep treatment process for the removal of dissolved oil.
Adsorption Method
The adsorption method utilizes porous solid adsorbents to adsorb the dissolved oil and other soluble organic substances in oily wastewater on the surface. The commonly used adsorbent activated carbon not only has good adsorption performance for oil, but also can effectively adsorb other organic substances in wastewater. However, its adsorption capacity is limited (usually 30-80mg/g for oil), and its high cost and difficulty in regeneration limit its application.
Adsorption resin is a new type of organic adsorption material developed in recent years, with good adsorption performance, easy regeneration and reuse, and is expected to replace activated carbon. In addition, fly ash, graphite, coal, oil absorbent felt, ceramsite, quartz sand, sawdust, straw, etc. also have oil absorption properties and can be used as adsorption materials. After oil absorption saturation, some adsorption materials can be renewable and reused, while others can be directly used as fuel.
After being treated by adsorption method, the oil content in the effluent can reach 5mg/L or even below 1mg/L. Therefore, adsorption method has its unique advantages as a deep treatment process for oily wastewater.
Visit www.evuchina.com for more informations!

#QDEVU #WATERTREATMENT #WASTEWATERTREATMENT #SEWAGETREATMENT #SEWAGEWATERTREATMENT #WATERFILTER #WATERFILTRATION #SLUDGETREATMENT #SLUDGEDEWATERING